The synchronizing monitor does not automatically
providing power to charge the system batteries. This
parallel two generators when it is connected to the
motor-generator condition exists when the ship's
system. The generators must be paralleled manually.
service power supply is meeting the voltage and
This is independent of whether or not the synchronizing
frequency requirements of the critical load.
monitor is connected to the circuit. The function of the
MG MODE 2
synchronizing monitor is to prevent the manual
paralleling of two generators when the phase angle,
Mode 2 operation of the motor-generator set (fig.
8-25, view B) represents the condition by which the set
voltage difference, and frequency difference of the two
receives power from the batteries, and the ac end of the
generators are not within safe limits.
set provides the power requirements for the critical load.
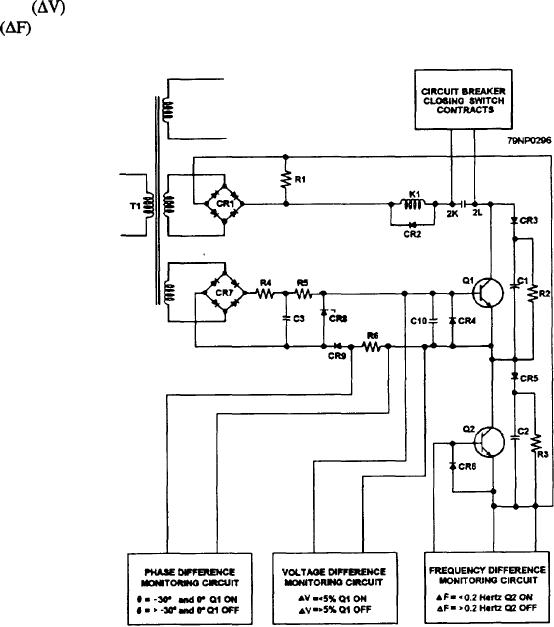
The synchronizing monitor consists of the
Mode 2 is referred to as the stop gap operation.
following four main circuits:
SYNCHRONIZING MONITOR
1. The output circuit
The synchronizing monitor (fig. 8-26) monitors the
2. The phase difference monitor circuit
phase angle, voltage, and frequency relationship
3. The frequency difference monitoring circuit
between the 450-volt, 60-Hz generator and an energized
bus. Circuits within this panel energize a relay when the
4. The voltage difference monitoring circuit
phase angle (0) is between -30 and 0, the voltage
OUTPUT CIRCUIT
difference
is less than 5 percent, or the frequency
The output circuit (fig, 8-27) contains the K1 relay,
drift
between an oncoming generator and an
its power supply, and a set of contacts (circuit breaker
energized bus is less than 0.2 Hz.
Figure 8-27.--0utput circuit.
8-35

