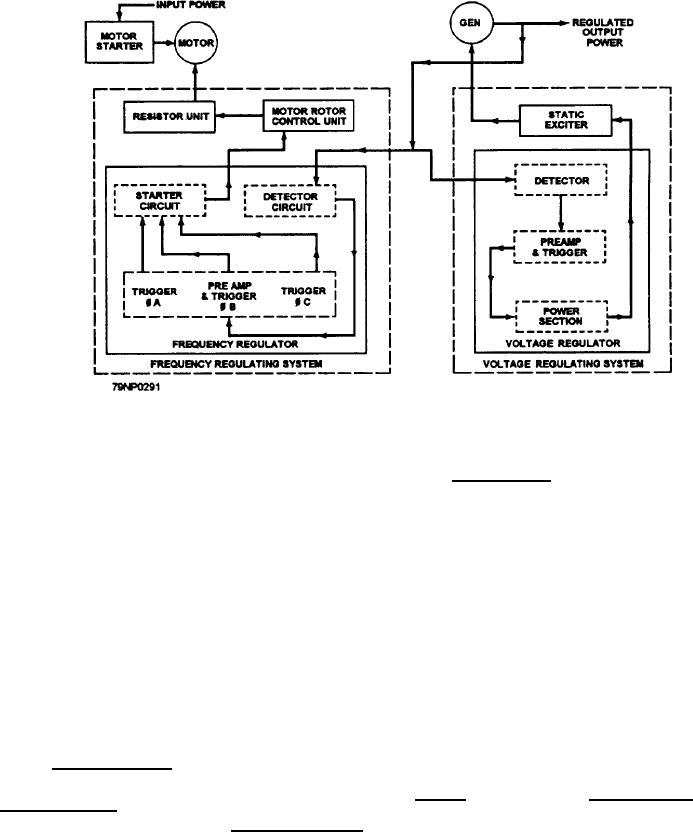
Figure 8-22.--Motor-generator set simplified block diagram.
3. A power section
controls the static exciter output. The static exciter
output, in turn, supplies dc (excitation current) to the
The detector circuit includes a sensing circuit and a
generator field of the proper magnitude so as to maintain
three-phase bridge rectifier. The sensing circuit consists
the generator output voltage within specified limits
of three voltage sensing transformers with their primary
under all load conditions.
windings connected to the generator output and their
The static exciter consists of the following
secondary windings connected to the bridge rectifier.
components:
The bridge rectifier provides a dc output voltage that is
proportional to the average of the three-phase voltage
1. A saturable current-potential transformer
outputs from the generator. This dc voltage is filtered
(SCPT)
and fed to a Zener reference bridge in the preamp and
2. Three linear reactors (chokes)
trigger circuit.
3. A three-phase bridge rectifier unit
The dc output from the detector is compared with a
The SCPT contains (1) a primary winding
constant Zener voltage in the reference bridge. The
consisting of both voltage and current windings, (2) a
difference (error) voltage output from the bridge is
dc control winding, and (3) a secondary winding. The
amplified by transistor amplifiers and fed to a
voltage primary windings are connected in series with
unijunction transistor circuit, which provides the pulses
the chokes across the generator output. The current
to trigger the SCRs in the power section. The SCR
primary windings are connected in series with the load,
output from the power section is fed to the control
and thus carry load current. The secondary winding
winding of the SCPT in the static exciter.
output is connected to the bridge rectifier unit, which
supplies the dc for the generator field. The SCPT
During starting, generator field current is supplied
control winding is connected to the output of the voltage
by a field flashing circuit, which is cut out after the
regulator.
generator builds up an output voltage. At no-load
voltage, the primary windings of the SCPT are
The voltage regulator consists of the following
energized through the choke coils and induce a voltage
components:
in the SCPT secondary windings. The rectified output
1. A detector circuit
of the secondary windings supplies the generator field.
This is the no-load field excitation.
2. A preamplifier (preamp) and trigger circuit
8-31

