CARE OF BRUSHES
All brush shunts should be securely connected to the
brushes and the brush holders. Brushes should move
freely in their holders, but they should not be loose
enough to vibrate in the holder. Before replacing a worn
brush with a new one, clean all dirt and other foreign
material from the brush holder.
Replace old brushes with new brushes when the old
brushes meet the following criteria:
worn or chipped so they will not move properly
in their holders
damaged shunts, shunt connections, or hammer
clips
riveted connections or hammer clips and are
worn to within one-eighth inch of the metallic
part
tamped connections without hammer clips, and
are worn to one-half or less of the original length
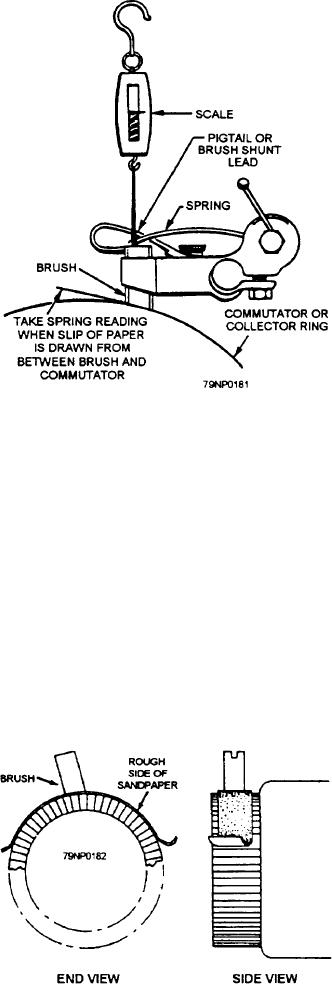
Figure 7-11.--Measuring brush tension.
of the brush; or
divided by the contact area maybe considered to be the
spring-enclosed shunts and are worn to 40
spring operating pressure.
percent or less of the original length of the brush
The toes of all brushes of each brush stud should
(not including the brush head, which fits into one
end of the spring).
line up with each other and with the edge of one
commutator segment.
Where adjustable brush springs are of the positive
gradient (torsion, tension, or compression) type, adjust
The brushes should be evenly spaced around the
them as the brushes wear to keep the brush pressure
commutator. To check brush spacing, wrap a strip of
approximately constant. Springs of the coiled-band,
paper around the commutator and mark the paper where
constant-pressure type, and certain springs of the
the paper laps. Remove the paper from the commutator,
positive gradient type are not adjustable except by
cut at the lap, and fold or mark the paper into as many
changing springs. Adjust pressure following the
equal parts as there are brush studs. Replace the paper
manufacturer's technical manual. Pressures as low as
on the commutator, and adjust the brush holders so that
1 1/2 psi of contact area may be specified for large
the toes of the brushes are at the creases or marks.
machines and as high as 8 psi of contact area may be
specified for small machines. Where technical manuals
are not available, a pressure of 2 to 2 1/2 psi of contact
area is recommended for integral horsepower and
integral kilowatt machines. About twice that pressure
is recommended for fractional horsepower and
fractional kilowatt machines. To measure the pressure
of brushes operating in box-type brush holders, insert
one end of a strip of paper between the brush and
commutator; use a small brush tension gage (such as the
0- to 5-pound indicating scale) to exert a pull on the
brush in the direction of the brush holder axis, as shown
in figure 7-11. Note the reading of the gage when the
pull is just sufficient to release the strip of paper so that
it can be pulled out from between the brush and
Figure 7-12.--Method of sanding brushes.
commutator without offering resistance. This reading
7-10

