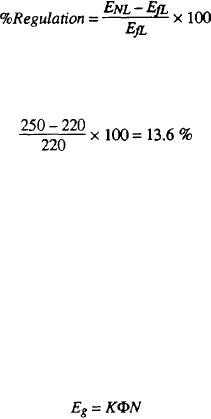
CHAPTER 8
VOLTAGE AND FREQUENCY REGULATION
Present ship's service generators and distribution
Sophisticated electronics and weapons systems
systems are adequate for 60- and 400-Hz type I power.
aboard modem Navy ships require closely regulated
Type II power differs principally from type I. Type II
electrical power for proper operation. The increased
has more stringent voltage requirements. Better voltage
demand for closely regulated power is being met by
regulation at the ship's service generator will not satisfy
establishing new standards for ac shipboard power
system. Also, new voltage and frequency-regulating
these voltage requirements. This is because the
specified voltage is at the equipment or load, not at the
equipment has been developed. Following a brief
generator output. Static type line voltage regulators
discussion of the new standards and equipment, this
which provide type II voltage control at the load are
chapter contains a discussion on the various types of
voltage regulators for ac generators in use aboard Navy
discussed in the chapter.
ships and the SPR 400 in-line regulator.
Voltage and frequency requirements for type III
power cannot be met without isolating the equipment
requiring the power from the rest of the power system.
LEARNING OBJECTIVES
Motor generator sets are normally used for this purpose.
Upon completion of this chapter you should be able
PRINCIPLES OF AC VOLTAGE
to do the following:
CONTROL
1. Recognize the need for voltage and frequency
The voltage regulation of an ac generator is the
regulation.
change of voltage from full load to no load, expressed
2. Recognize the types of power used aboard ship,
in percentage of full-load volts, when the speed and dc
and identify their use.
field current are held constant.
3. Identify the characteristics of the components
used in various voltage and frequency
regulators.
For example, the no-load voltage of a certain
4. Recognize the operation of various voltage and
generator is 250 volts, and the full-load voltage is 220
frequency regulators in use today.
volts. The percent of regulation is
5. Troubleshoot various voltage and frequency
regulators by observing their operation.
6. Recognize the approved servicing techniques
In an ac generator, an alternating voltage is induced
for transistorized circuits.
into the armature windings when magnetic fields of
alternating polarity are passed across these windings.
The amount of voltage induced into the ac generator
TYPES I, II, AND III POWER
windings depends mainly on the number of conductors
in series per winding, the speed at which the magnetic
MIL-STD-761B (Ships) of 15 July 1965 established
field passes across the winding (generator rpm), and the
standard electrical characteristics for ac power systems.
strength of the magnetic field Any of these three factors
The three basic power supplies (types I, II, and III) are
could be used to control the amount of voltage induced
described in table 8-1. The power system
into the ac generator windings.
characteristics shown are those existing at the load.
They do not represent generator output characteristics.
This can be represented by the following formula:
All figures are the maximum allowable percentages or
times for that type power.
8-1

