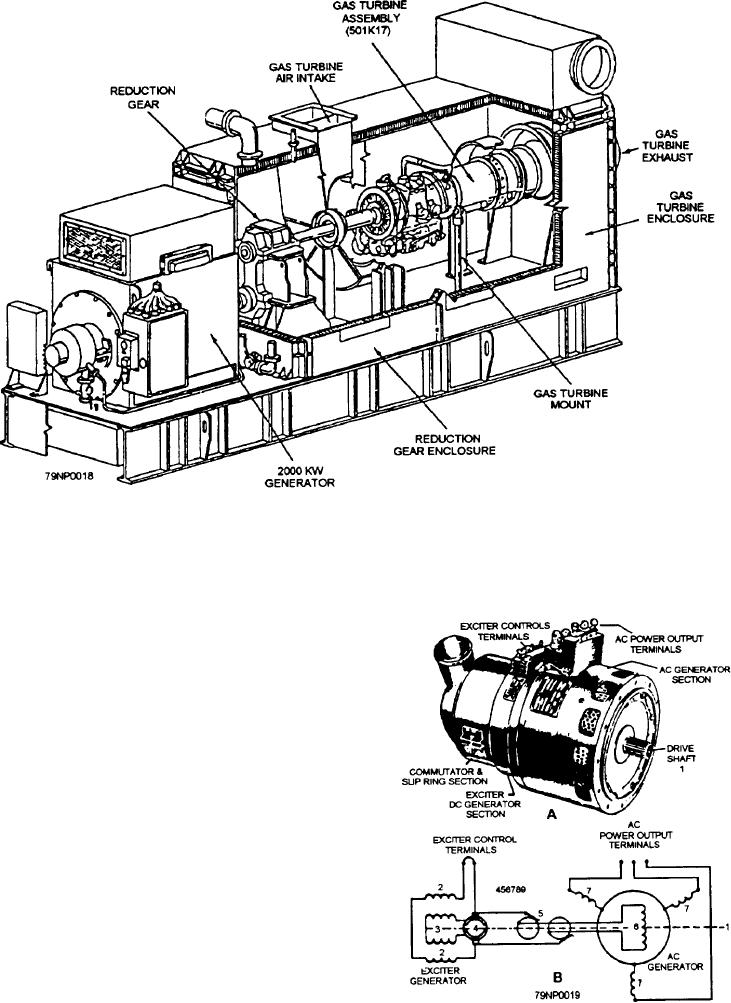
Figure 3-18.--Model 104 gas turbine generator set.
generator through the rotor drive shaft (1) (view A). The
electrical power. The gas turbine units (fig. 3-18) are
exciter shunt field (2) (view B) creates an area of intense
small, efficient, easily replaed, and simple to operate.
While Gas Turbine Specialist's (GS's) are primarily
responsible for maintenance on the unit itself, EM's
often stand electrical watch on the units.
Basic Functions of Generator Parts
A typical rotating-field ac generator consists of an
ac generator and a smaller dc generator built into a single
unit. The ac generator section supplies alternating
current to the load for which the generator was designed.
The dc generator supplies the direct current required to
maintain the ac generator field. This dc generator is
referred to as the exciter. Atypical ac generator is shown
in figure 3-19, view A. Figure 3-19, view B, is a
simplified schematic of the generator. The parenthetical
numbers in the following paragraph are indicated on
figure 3-19.
Operation
Any rotary generator (fig. 3-19) requires a prime
moving force to rotate the ac field and exciter armature.
This rotary force is usually furnished by a combustion
Figure 3-19.--An ac generator and schematic.
engine, turbine, or electric motor and transmitted to the
3-15

