length of time. The rating of a generator is identified
Revolving Field
very closely with its current capacity.
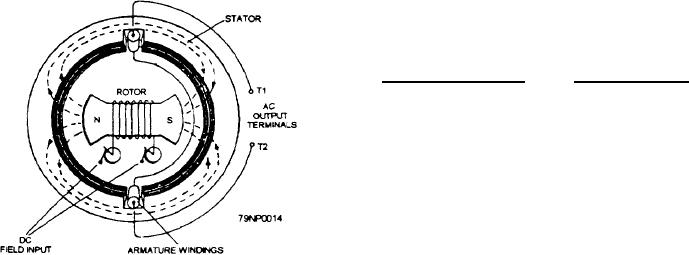
The rotating-field ac generator (fig. 3-14) is the
Temperature
most widely used type of generator. The rotating
magnetic field produced by the rotor extends outward
The rating of any electric device must take into
and cuts through the armature windings imbedded in the
account its allowable temperature rise; that is, the
surrounding stator. As the rotor turns, alternating
amount of rise in temperature (above ambient) the
voltages are induced in the windings since magnetic
machine can withstand and still be expected to operate
fields of first one polarity and then the other cut through
normally. The load rating of a particular generator is
them. Since the output power is taken from stationary
determined by the rise in temperature it can withstand,
windings, the output may be connected through fixed
caused primarily by the current flow. The rise in
terminals (T1 and T2 in fig. 3-14). This is helpful
temperature is caused by the losses of the generator. The
because there are no sliding contacts, and the whole
majority of losses are 12R losses in the armature
output circuit is continuously insulated, reducing the
windings.
danger of arc-over.
The maximum current that can be supplied by an ac
The rotating-field ac generator maybe constructed
generator depends upon the following factors:
with or without brushes. In both types, dc from a
1. The maximum heat loss (I2R power loss) that
separate source is passed through windings on the rotor
cart be sustained in the armature, and;
to develop the rotating magnetic field. The source of dc
may be a permanent magnet generator with its output
2. The maximum heat loss that can be sustained in
going to the rotor winding slip rings through a
the field.
commutator (fig. 3-15, view A) or an alternator with its
The armature current varies with the load and is
output rectified by a silicon rectifier (fig. 3-15, view B)
similar to that of dc generators. In ac generators,
before being sent to the rotor.
lagging power factor loads tend to demagnetize the
Slip rings and brushes or silicon rectifier units are
field. The terminal voltage is maintained only by an
adequate for the dc field supply because the power level
increase in the dc field current. Therefore, ac generators
in the field is much smaller than in the armature circuit.
are rated for armature load current and voltage output,
or kilovolt-ampere (kVA) output, at a specified
frequent y and power factor.
RATING OF AC GENERATORS
Power Factor
Alternators are rated according to the voltage and
current they are designed to produce. The normal load
The power factor is an expression of the losses
rating is the load it cart carry continuous y. The overload
within the electrical distribution system. It is
rating is the above normal load it cart carry for a specific
determined by the amount the current and voltage sine
waves are out of phase, which is determined by the
characteristics of the total load seen on the circuit
(resistive, inductive, or capacitive). The power factor
can be found by using two methods:
Algebraic Method
Trigonometric Method
Determine true power (kW)
Determine the angle of lead
or lag between voltage and
consumed by load from
current
Power factor is cosine of
Determine apparent power
(kVA) consumed by load
phase angle
by multiplying line voltage
and current from meters on
swbd
Power Factor = kW/kVA
Figure 3-14.--Essential parts of a rotating-field generator.
3-12

