When all three-phase voltages are balanced, the flux
Circuit breakers are available in manually or
electrically operated types. Some types may be
produced by winding 1-2 is exactly equal and opposite
operated both ways, while others are restricted to one
to that produced by winding 2-3. The flux produced by
mode. Manually or electrically operated types may or
winding 1-3 is exactly equal and opposite to that
may not provide protective functions. The differences
produced by the other 2-3 winding. Therefore, the
and uses of the various types of circuit breakers are
resultant flux is zero, and no magnetic pull is exerted on
described in the following sections.
the armature of the relay.
If a short circuit is placed across lines 1 and 2, no
ACB
flux is produced by winding 1-2. This means that the
flux produced by one of the 2-3 windings is no longer
balanced, and there is a resultant flux, which exerts pull
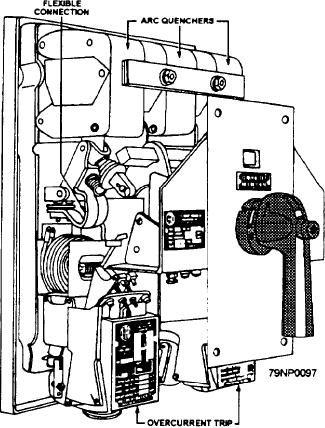
The ACB type of circuit breaker maybe for either
on the relay armature. The armature moves until the
manual local closing or electrical remote closing. It has
moving contact hits stationary contact 2 (fig. 2-48, view
an open metallic frame construction mounted on a
B). This action opens the circuit between the moving
drawout mechanism and is normally applied where
contact and stationary contact 1. As soon as the short
heavy load and high short-circuit currents are available.
circuit is removed from lines 1 and 2, the resultant flux
Figure 2-50 shows the external view of a type ACB
circuit breaker.
is zero, which allows the spring to return the armature
to its original position. Similarly, if shorts occur on lines
2 and 3 or lines 1 and 3, the resultant flux is no longer
zero, and the relay will operate.
Never open the dc circuit to the Rectox unit while
the voltage is being applied to the ac side. This
precaution is necessary because the voltage across the
Rectox is only a small portion of the total voltage drop
due to the reactor being in the circuit. If the dc side is
opened, full voltage is applied across the unit, which
may cause the unit to break down.
Very little maintenance is required for this relay. No
lubrication is needed. However, the relay must be kept
clean so that dirt and dust will not interfere with its
operation.
Because the relay rarely operates, check its
operation every month or two as recommended by
Naval Ships' Technical Manual, chapter 320.
CIRCUIT BREAKERS
The purposes of circuit breakers are normal
switching operation, circuit protection, and circuit
isolation.
Air circuit breakers are used in switchboards, switch
gear groups, and distribution panels. The types installed
on naval ships are ACB, AQB, AQB-A, AQB-LF,
NQB-A, ALB, and NLB. They are called air circuit
breakers because the main current-carrying contacts
Figure 2-50.--Type ACB circuit breaker.
interrupt in air.
2-42

