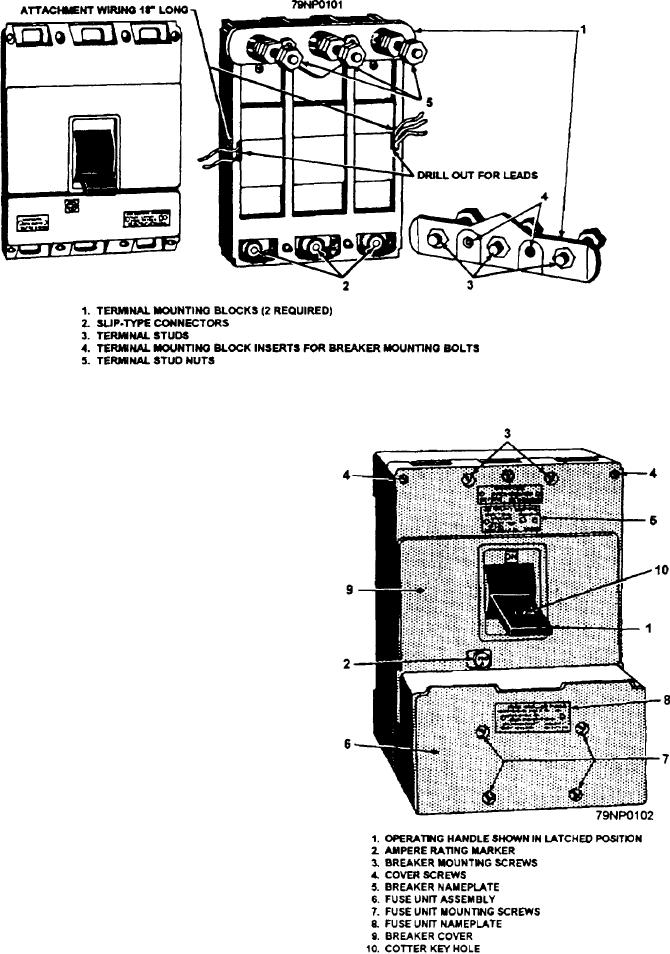
Figure 2-54.--AQB-A250 circuit breaker, rear view, with terminal mounting blocks.
(fig. 2-54) for drawout mounting consist of terminal
studs in terminal mounting blocks of insulating material.
The terminals of the circuit breaker have slip-type
connectors, which engage the terminal studs as shown
in figure 2-54. Two mounting blocks are usually
required for each circuit breaker. This method of
connecting a circuit breaker to a bus or circuit is known
as a back-connected circuit breaker. Circuit breakers
that have solderless connectors attached to their
terminals are commonly called front-connected circuit
breakers. The interrupting rating of the AQB-A250
circuit breaker is 20,000 amperes at 500 volts ac, 60
hertz; 10,000 amperes at 500 volts ac, 400 hertz; or
15,000 amperes at 250 volts dc.
AQB-LF250
The AQB-LF250 circuit breaker (fig. 2-55)
combines the standard AQB circuit breaker and a
current-limiting fuse unit, which interrupts the circuit
when the current is in excess of the interrupting rating
of the breaker. Constructed as one compact unit, the
AQB-LF circuit breaker incorporates the
current-limiting fuses (fig. 2-56) as integral parts of the
circuit breaker. The common trip features and trip units
in this type of circuit breaker are identical to those in the
AQB-A250 circuit breakers.
The current-limiting fuse unit is designed so that it
trips the breaker and opens all poles if any
Figure 2-55.--AQB-LF250 complete circuit breaker, front view.
current-limiting fuse (fig. 2-57) is blown. After a fuse
2-46

