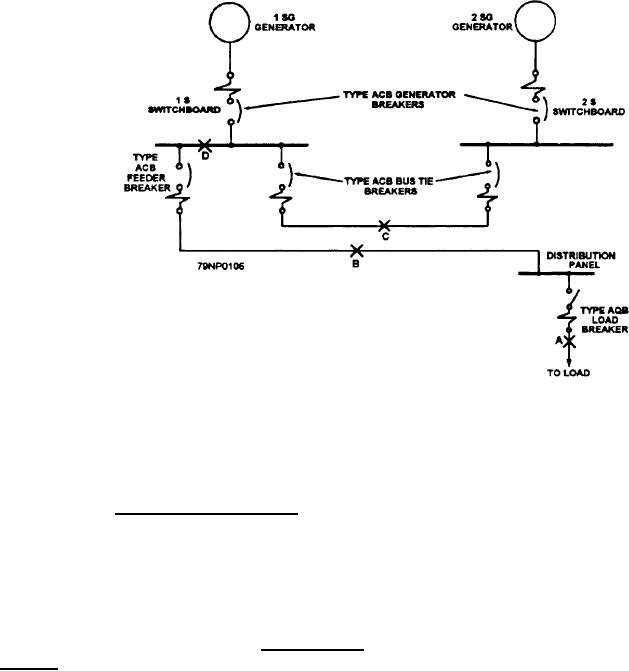
Figure 2-59.--Selected tripping of circuit breakers.
Selective tripping of breakers is normally obtained
Refer to figure 2-59. Assume that a fault or defect
by a short time-delay feature. This feature is a
develops in the cable insulation at point A. An
mechanical time delay and can be varied with
overcurrent flows through the AQB load circuit breaker
and the ACB feeder circuit breaker. The AQB load
limitations. The generator circuit breaker, which is
breaker will open the circuit and interrupt the current in
closest to the power source, has the maximum
an interval of time that is less than the time required to
continuous current-carrying rating, the highest available
open the ACB feeder circuit breaker. Thus, the ACB
short-circuit current rating, and the maximum short time
feeder breaker will remain closed when the AQB
delay trip. This allows the generator breaker to be the
breaker clears the circuit. However, if the fault current
last breaker to trip. However, it will trip on the generator
should exceed the interrupting capacity of the AQB load
short-circuit current at some definite interval of time
breaker (for example, an excess of 10,000 amperes), this
within the tolerance of the breaker. Bus tie circuit
breaker would be unable to interrupt the fault current
breakers are usually set to trip after a prescribed time
without damage to the breaker. To prevent damage to
delay that is less than the generator circuit breaker set
the AQB load breaker, the ACB feeder breaker (on
time delay.
switchboard 1S) serves as a backup breaker for the
The construction of circuit breakers for selective
AQB load breaker and will open almost instantaneously.
tripping for currents less than the instantaneous trip
current setting causes an intentional delay in the
A fault at point B with overcurrent would trip the
ACB feeder breaker in time but not the ACB generator
operation of the breaker. The time delay is greater for
or bus tie breakers. They require longer time intervals
small currents than for large currents and is therefore
in which to trip.
known as an inverse time delay. The current that would
trip the AQB load circuit breaker instantaneous] y and
A fault at point C with overcurrent would trip both
clear the circuit will not trip the ACB feeder circuit
ACB bus tie breakers.
breaker unless the current flows for a greater length of
time. The same sequence of operation occurs for the
A fault at D with overcurrent on switchboard 1S
other groups of circuit breakers adjusted for selective
would trip the associated ACB generator breaker and
tripping in the system. The difference between the
one or both of the ACB bus tie breakers.
tripping times of the breakers is sufficient to permit each
breaker to trip and clear the circuit before the next
In each case, the faulty section of the system is
breaker starts to operate.
isolated, but power is maintained on as much of the
2-51

