OMEGA BASICS
ADVANTAGES
OMEGA is a hyperbolic phase-difference
measurement system. Hyperbolic navigation involves
comparing the phase angles of two or more radio
signals that are synchronized to a common time base.
By moving the OMEGA receiver (by ship’s
movement) and keeping the transmitter stations on
frequency with a constant difference in time and
phase, the system can measure the relative phase
relationship between two stations to determine a line
of position (LOP) for the ship. The relative phase
angle measured between paired transmitting stations
depends upon the distance of the receiver from each
t r a n s m i t t e r .
It is important to understand that a minimum of
two transmitters are required to obtain a basic position
fix. Three or four are necessary to obtain an accurate
fix. Unfortunately, there are many times in which
only two transmitters are available but three are
desired. One way around this problem is to use the
receiver oscillator as a third, or “phantom,”
transmitter. By setting the receiver oscillator to the
frequency transmitted by each of the two OMEGA
transmitters, the operator can compare the actual
transmitted frequencies to the frequencies of the two
received signals.
This comparison provides two
phase angles. The operator can then compare the two
phase angles to determine a third phase angle. The
three phase angles will yield a fix as accurate as a fix
determined from three actual transmitters.
SHIP’S INERTIAL
NAVIGATION SYSTEM
The Ship’s Inertial Navigation System (SINS) is
a navigation system that (after initial latitude,
longitude, heading, and orientation conditions are set
into the system) continuously computes the latitude
and longitude of the ship by sensing acceleration.
This is in contrast to OMEGA and LORAN, which fix
the ship’s position by measuring position relative to
some known object. SINS is a highly accurate and
sophisticated dead reckoning device. Let’s look at
some of the advantages of using the SINS.
SINS has a major security advantage over other
types of navigation systems because it is completely
independent of celestial, sight, and radio navigation
aids. In addition, SINS has the following advantages:
1. It is self-contained.
2. It requires minimal outside
information.
3. It cannot be jammed.
4. It is not affected by adverse weather
conditions.
5. It does not radiate energy.
6. It is not detectable by enemy sensors.
Now that we have seen the advantages of this
system, let’s look at its basic components.
BASIC COMPONENTS
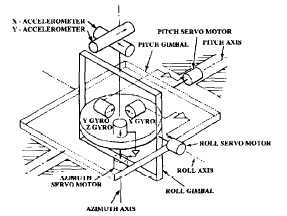
Look at figure 1-1. The basic components of an
inertial navigation system are accelerometers,
gyroscopes, servo systems, and the computers (not
shown). Accelerometers measure changes in speed or
direction along the axis in which they lie. Their
output is a voltage, or series of pulses (digital),
proportional to whatever acceleration is experienced.
Figure 1-1.—Stable platform with inertial components.
1-3