If the particular address is found in the cache, the
block of data is sent to the CPU, and the CPU goes about
its operation until it requires something else from
memory. When the CPU finds what it needs in the
cache, a hit has occurred. When the address requested
by the CPU is not in the cache, a miss has occurred and
the required address along with its block of data is
brought into the cache according to how it is mapped.
Cache processing in some computers is divided into
two sections: main cache and eavesdrop cache. Main
cache is initiated by the CPU within. Eavesdrop is done
when a write to memory is performed by another
requestor (other CPU or IOC). Eavesdrop searches
have no impact on CPU performances.
CACHE MAPPING TECHNIQUES.— Cache
mapping is the method by which the contents of main
memory are brought into the cache and referenced by
the CPU. The mapping method used directly affects the
performance of the entire computer system.
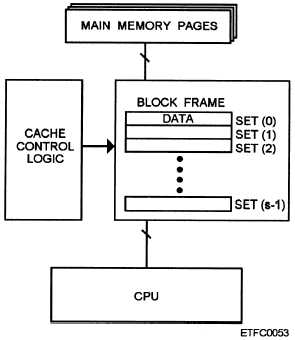
. Direct mapping —Main memory locations can
only be copied into one location in the cache. This is
accomplished by dividing main memory into pages that
correspond in size with the cache (fig. 5- 10).
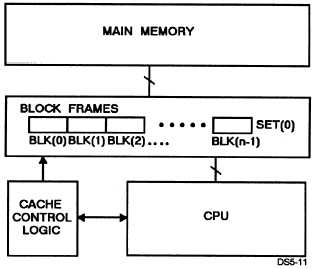
l Fully associative mapping —Fully associative
cache mapping is the most complex, but it is most
flexible with regards to where data can reside. A newly
read block of main memory can be placed anywhere in
a fully associative cache. If the cache is full, a
Figure 5-10.—Example of direct mapping used in cache
memory.
Figure 5-11.—Example of fully associated mapping used in
cache memory.
replacement algorithm is used to determine which block
in the cache gets replaced by the new data (fig. 5-11).
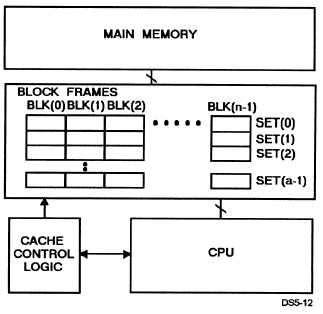
l Set associative mapping —Set associative cache
mapping combines the best of direct and associative
cache mapping techniques. As with a direct mapped
cache, blocks of main memory data will still map into
as specific set, but they can now be in any N-cache block
frames within each set (fig. 5-12).
CACHE READ.— The two primary methods used
to read data from cache and main memory are as
follows:
Figure 5-12.—Example of set association mapping used in
cache memory.
5-16