Figure 2-15.--Measuring insulation resistance of a power circuit.
de-energized in a warm ambient, and 40F if it is
In power circuits (fig. 2-15), include the legs or
de-energized in a cold ambient.
phase leads, panel wiring terminals, connection boxes,
fittings, and outlets (plugs removed).
Look at figure 2-17, which shows a nonograph for
obtaining resistance per foot. Select the point of
For degaussing circuits, you should take
allowable resistance per foot based on the ambient
measurements at a degaussing coil connection box;
condition and the type of cable. Using the nomograph,
include in the legs measured the coil cables, through
draw a straight line from the measured insulation
boxes, and feeder cables. Disconnect the supply and
resistance to the length of cable. The line should cross
control equipment by opening the circuit on the coil side
the resistance per foot line above the selected minimum
Measure the
of the control equipment.
resistance per foot point. Corrective action is required
compass-compensating coil feeder cable with all control
if the resistance per foot is less than the selected point.
equipment disconnected. Additional information on
tests of degaussing installations is obtained in NSTM,
chapter 475, and in the degaussing folder furnished with
each degaussing installation.
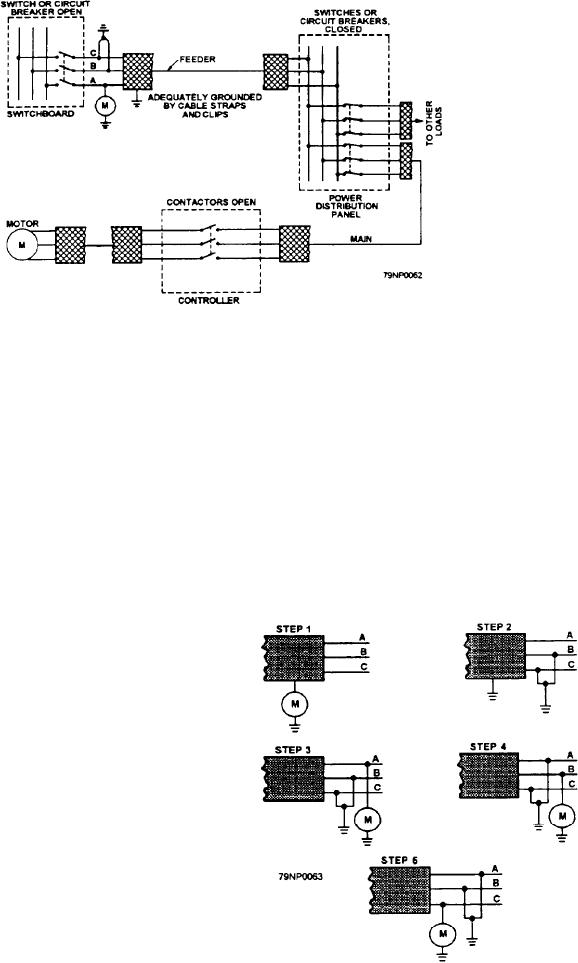
As you use the table, refer to figure 2-16. You
should make measurements of the lighting, power, and
degaussing circuits as shown in table 2-7.
These resistance measurements are considered
satisfactory if they are not less than 1 megohm for each
complete power circuit or at least 0.5 megohm for each
complete lighting circuit. Circuits that have been
de-energized for at least 4 hours are classed as either
warm ambient or cold ambient.
NOTE: A warm ambient is defined as a warm
climate or a condition in which the entire cable is in a
heated space and not in contact with the ship's hull. A
cold ambient is defined as a cold climate or a condition
in which most of the cable is in an unheated space or is
against the ship's hull in cold waters.
The cable temperature should be considered to be 104F
Figure 2-16.--Measuring circuit insulation resistance.
if the cable has been energized for 4 hours, 70F if it is
2-18

