CHAPTER 5
ELECTRICAL AUXILIARIES
Electrician's Mates (EMs) are required to maintain
various types of electrical equipment aboard ship. This
chapter will introduce you to the operating principles of
some of the most widely used types of auxiliary
equipment and describe methods and procedures for
operating and maintaining them.
LEARNING OBJECTIVES
Upon completing this chapter, you will be able to
do the following:
1. Identify proper use and care of dc systems
including batteries, battery chargers, and small
craft starting system.
2. Identify the operating characteristics and
procedures for maintaining air conditioning,
refrigeration, and air compressor units.
3. Identify the care of and the maintenance
procedures for vent fog precipitators.
4. Identify the proper operating and maintenance
procedures for various deck equipment.
5. Identify proper operating and troubleshooting
techniques for maintaining electrohydraulic
6. Identify the operating characteristics of various
galley and laundry equipment.
STORAGE BATTERIES
Lead-acid storage batteries provide a cheap,
portable, rechargeable source of dc power. Batteries
have many uses including starting small boat engines
and acting as a source of backup power for the ship's
gyro. The battery also functions as a voltage stabilizer
in the small craft electrical system and supplies
electrical power for a limited time when the electrical
load exceeds the output of the boat's generator.
CONSTRUCTION
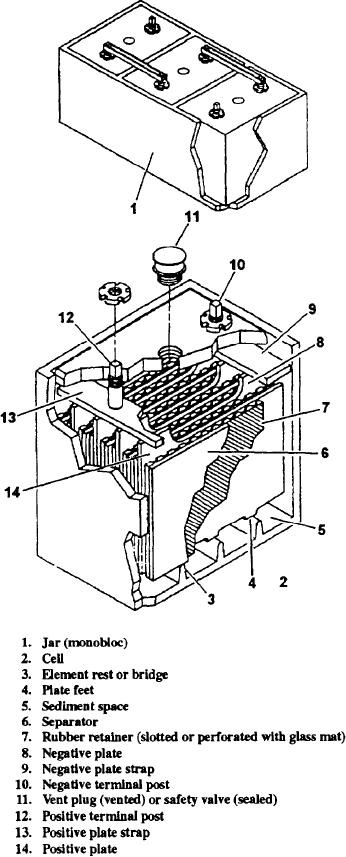
No matter the number of cells, lead-acid batteries
used in the Navy are basically the same in construction
and operation. The following components make up a
Figure 5-1.--Three-cell (6V) lead-acid battery.
typical lead-acid storage battery (fig. 5-1).
5-1

