control signal to the appropriate DFCS linear switch
assembly, which will respond with a status signal when
it is in the assigned position. The PBI will light when
the switch is in the commanded position.
Four colors are used for PBI indicators: white, red,
green, and yellow.
White indicates the linear slide
switch position is in the ON position. Red indicates the
switch is in the OFF position Green indicates the
switch is in the NORMAL position, while yellow
indicates the switch is in the ALTERNATE position.
Figure 5-14 shows an example of a typical CSCP
configuration. The number and functional assignment
of PBIs vary from ship to ship.
The PBIs in the lower-right corner of the CSCP front
panel shown in figure 5-14 are used to apply power to
the CSCP PBIs (ON), to indicate current CSCP control
status (CSCP CONTROL or ALT CSCP CONTROL),
and to transfer control from the controlling CSCP to the
alternate CSCP (REQ CONTROL, HOLD, ALT CSCP
REQ CONTROL, and ALT CSCP HOLD). Manual PBI
actions are required at both CSCPs to transfer control
between panels.
At the requesting CSCP, depression of the REQ
CONTROL PBI will cause the ALT CSCP REQ
CONTROL indicator to light red on the controlling
CSCP. The REQ CONTROL PBI will flash red on the
requesting CSCP until the operator of the controlling
CSCP depresses ALT CSCP CONTROL PBI, giving
control to the requesting CSCP. The CSCP CON-
TROL light will come on when the requesting CSCP
is in control and the flashing light will go out. The
HOLD PBIs are used to indicate refusal to transfer
control.
SHIP, SWITCHBOARD, AND
COMPUTER SWITCHING
CONTROL PANEL (CSCP)
WIRING
Switchboard and CSCP wires are those wires
connecting assemblies and components inside the
switchboard and CSCP. Ships cables are individually
plug-connected to panel connectors in the switchboard.
Ships cables are identified by a cable group number and
cable type.
Ships cables, switchboard wires, and CSCP harness
wires use plastic sleeves or metal tags for marking.
Each ship wire has a marking bearing the wire number.
When required, switchboard and CSCP wires have
plastic marking sleeves at each end. The sleeves
identify the terminals at both ends of the wire. Separate
wiring codes are used for ships wires, switchboard
wires, and CSCP wires.
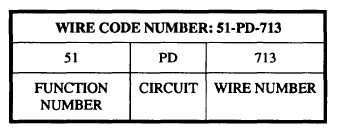
The ships wire marking codes are system oriented.
They consist of an alphanumeric code that identifies the
signal being carried by function number, circuit
designation, and assigned wire number. Atypical ships
wire code number is shown in table 5-1.
Table 5-1.-A Typical Ships Wire Marketng Code Number
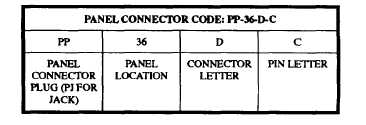
Eight types of PANEL ASSEMBLY connectors are
used in the switchboard. These connectors are used for
the linear movement switch assemblies, fuse tester
assembly, relay tester assembly, and power distribution
assembly. They consist of various types of 120-, 117-,
104-,85 -,38-,20-,10-, and 3-pin connectors. For wiring
and maintenance purposes, a common alphanumeric
designation system is used to identify specific circuit
connections, as shown in table 5-2.
Table 5-2.-Panel Connection Cable Code
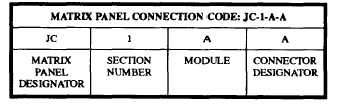
Located within the switchboard are panels known
as matrix panels. The matrix panels interconnect the
signal paths between the ships wiring and the assembly
panels. The designation codes for matrix panel
connections are shown in table 5-3.
Table 5-3.-Matrix Panel Connection Code
Intersection connectors are used to tie switchboard
sections together.
Intersection connector codes are
identified in table 5-4.
5-10