efficient way to transfer electromagnetic energy.
WAVEGUIDES are essentially coaxial lines without
center conductors.
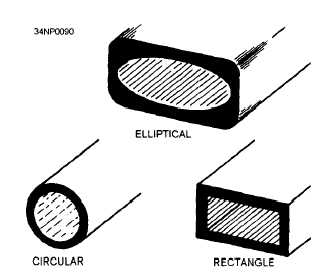
They are constructed from
conductive material and may be rectangular, circular,
or elliptical in shape, as shown in figure 3-17.
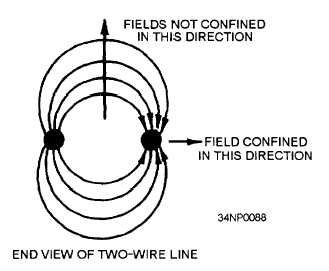
Figure 3-15.—Fields confined in two directions only.
Figure 3-16.—Fields confined in all directions.
WAVEGUIDE ADVANTAGES
Waveguides have several advantages over two-wire
and coaxial transmission lines. For example, the large
surface area of waveguides greatly reduces COPPER
(12R) LOSSES. Two-wire transmission lines have large
copper losses because they have a relatively small
surface area. The surface area of the outer conductor
Figure 3-17.—Waveguide shapes.
of a coaxial cable is large, but the surface area of the
inner conductor is relatively small. At microwave
frequencies, the current-carrying area of the inner con-
ductor is restricted to a very small layer at the
surface of the conductor by an action called SKIN
EFFECT.
Skin effect tends to increase the effective resistance
of the conductor. Although energy transfer in coaxial
cable is caused by electromagnetic field motion, the
magnitude of the field is limited by the size of the
current-carrying area of the inner conductor. The small
size of the center conductor is even further reduced
by skin effect, and energy transmission by coaxial
cable becomes less efficient than by waveguides.
DIELECTRIC LOSSES are also lower in waveguides
than in two-wire and coaxial transmission lines.
Dielectric losses in two-wire and coaxial lines are
caused by the heating of the insulation between the
conductors. The insulation behaves as the dielectric
of a capacitor formed by the two wires of the
transmission line. A voltage potential across the two
wires causes heating of the dielectric and results in
a power loss. In practical applications, the actual
breakdown of the insulation between the conductors
of a transmission line is more frequently a problem
than is the dielectric loss.
This breakdown is usually caused by stationary
voltage spikes or “nodes,” which are caused by
standing waves. Standing waves are stationary and
occur when part of the energy traveling down the line
3-9