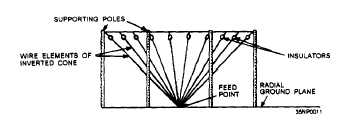
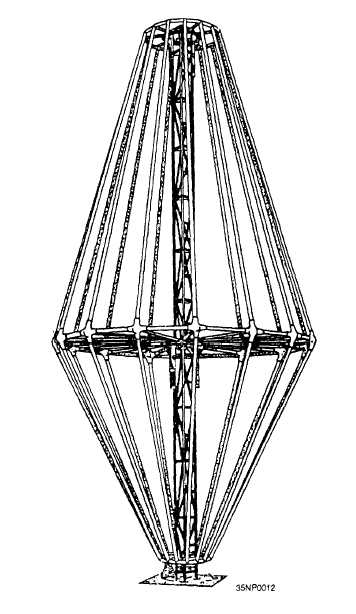
Figure 2-19.—Inverted cone antenna.
greater than 2:1. They are considered medium- to
high-power radiators, with power handling capabilities
of 40 kW average power.
CONICAL MONOPOLE ANTENNA
Conical monopoles are used extensively in hf
communications. A conical monopole is an efficient
broadband, vertically polarized, omnidirectional antenna
in a compact size. Conical monopoles are shaped like
two truncated cones connected base-to-base. The basic
conical monopole configuration, shown in figure 2-20,
is composed of equally-spaced wire radiating elements
arranged in a circle around an aluminum center tower.
Usually, the radiating elements are connected to the
top and bottom discs, but on some versions, there is
a center waist disc where the top and bottom radiators
are connected. The conical monopole can handle up
to 40 kW of average power. Typical gain is -2 to +2
dB, with a vswr of up to 2.5:1.
RHOMBIC ANTENNA
Rhombic antennas can be characterized as
high-power, low-angle, high-gain, horizontally-
polarized, highly-directive, broadband antennas of
simple, inexpensive construction. The rhombic antenna
(fig. 2-21) is a system of long-wire radiators that
depends on radiated wave interaction for its gain and
directivity. A properly designed rhombic antenna
presents to the transmission line an input impedance
insensitive to frequency variations up to 5:1. It
maintains a power gain above 9 dB anywhere within
a 2:1 frequency variation.
At the design-center
frequency, a gain of 17 dB is typical. The radiation
pattern produced by the four radiating legs of a
rhombic antenna is modified by reflections from the
earth under, and immediately in front of, the antenna.
Because of the importance of these ground
Figure 2-20.—Conical monopole antenna.
reflections in the proper formation of the main lobe,
the rhombic should be installed over reasonably smooth
and level ground.
The main disadvantage of the
rhombic antenna is the requirement for a large land
area, usually 5 to 15 acres.
QUADRANT ANTENNA
The hf quadrant antenna (fig. 2-22) is a
special-purpose
receiving
antenna
used
in
ground-to-air-to-ground communications. It is unique
among horizontally-polarized antennas because its
2-11