Large-scale integration (LSI)-ICs with more
than 100 gates.
Very large-scale integration (VLSI)-ICs with
more than 1000 gates.
IC FAMILIES
The types of IC families are identified by the dif-
ferent ways in which the elements are connected and by
the types of elements used (diodes, resistors, transistors,
and the like). The two families of ICs in widespread use
today are bipolar and metal-oxide semiconductor (MOS).
They can be used in both digital and linear ICs. They
can also be combined on the same IC chip to obtain the
advantages from each technology. ICs that combine the
technology of bipolar and MOS are referred to as Bipolar
MOS (BIMOS). Refer to the glossary for a brief de-
scription of bipolar, MOS, and BIMOS if you need to.
IC CATEGORIES
To perform their functions, digital computers use
two broad categories of ICs—digital and linear. Digital
ICs contain switching-type circuitry. Linear ICs con-
tain amplifying-type circuitry. You can say that the
computer uses digital ICs to perform the decision-
making functions internally and linear ICs to perform
the regulating and sensing functions internally and
externally. The digital and linear ICs rely on and work
with each other. Most ICs contained in a computer are
digital; hence, the computer is referred to as being
digital. The larger building blocks of the computer will
use these smaller building blocks that digital and linear
ICs provide to perform the functions of the computer.
TOPIC 4—DIGITAL IC’S
Digital ICs handle digital information by means of
switching circuits. They can also be used to control and
regulate power for working devices such as a power
supply. Digital ICs are used to process and store
information in computers.
DIGITAL IC FAMILY TYPES
Digital IC family types include bipolar and
metal-oxide semiconductors.
Bipolar ICs
Digital bipolar ICs include:
l DTL (Diode-Transistor-Logic)
l TTL (Transistor-Transistor Logic), the most
widely used packaged IC. Variations of TTL
include TTL-H (high-speed TTL), TTL-S
(TTL-Schottky), and
TTL-S)
ECL (emitter coupled
(current mode logic)
LP TTL-S (low-power
logic), also called CML
IIL or I2L (Integrated injection logic)
Advanced Schottky (AS)
Advanced Low-Power Schottky (ALS)
See figure 4-4 for example schematics of bipolar ICs.
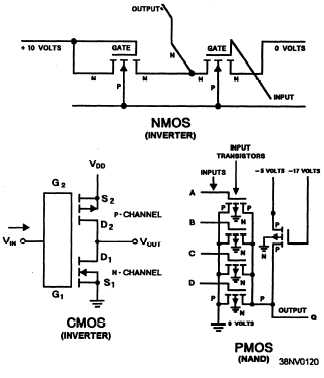
Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor (MOS) ICs
Digital MOS ICs include:
CMOS (Complementary
conductor)
NMOS (N-channel MOS)
PMOS (P-channel MOS)
CD (CMOS Digital)
metal-oxide semi-
TTLC (Bipolar TTL series in CMOS tech-
nology)
QMOS (Quick MOS)
HCMOS (High-Speed CMOS)
See figure 4-5 for example schematics of MOS ICs.
Figure 4-5.—Example schematics of MOS ICs.
4-7