The magnetic disk recorder/reproducer (RD) or
disk unit controller contains the circuitry to control the
reading and writing of data on a disk pack. It also
controls the interface with the computer. The disk unit
can control from one to four memory units (disk packs).
The memory units (MUs) contain only the logic
circuitry to record data on and read data from their own
disk packs. They do not contain controllers. They
operate only as slave units to the disk unit controller.
MAGNETIC DISK PACKS
The recording medium for a magnetic disk memory
set is a removable disk pack made up of one to over ten
14-inch disks, depending on the type.
Disk Pack Construction
The disks are coated with magnetic iron oxide. The
top and bottom platters of some disk packs are used as
protection for the inner disks recording surfaces. The
disk pack comes with a storage canister consisting of a
top and bottom cover as shown in figure 10-10. The top
cover is used to install the disk pack in the desired disk
or memory unit and to remove the disk pack from a unit
for storage. The bottom cover is removed just before
installation of the disk pack and replaced after the disk
pack has been removed from a unit to protect the disk
pack from physical damage and contamination.
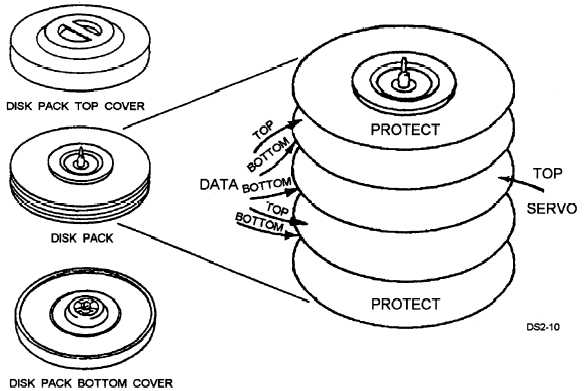
Disk Pack Data Surfaces
Looking at a disk pack with five platters, the top
and bottom platters are used to protect the six inside
surfaces (fig. 2-10). Five of the six inner disk surfaces
are used for data storage. Each recording surface
contains 823 tracks.
Of the 823 tracks, 822 are
addressable and can be used for data storage with the
remaining track being used for maintenance
applications. The tracks occupy a 2-inch band around
the circumference of the disk’s recording surface. The
individual tracks are .0026-inches apart. Each track can
store 6,038 BPI with a storage capacity per disk pack (5
recording surfaces) of 640 million bits (megabits).
Disk Servo Surface
The sixth surface, called the servo surface, contains
prerecorded dibits used to control the movement of the
read/write heads to the desired position (cylinder) on
the recording surfaces, and to maintain alignment of the
read/write heads over the centerline of the track. Dibit
is an abbreviation of a dipole bit. It is an analog bit with
a positive or negative signal used to indicate odd or even
tracks on the disk. As the read-only servo head moves
Figure 10-10.—A disk pack and storage canister.
10-14