paper. Because the toner is melted to the paper, the print
appears very smooth and loses the appearance of dots
that are common with dot matrix printers.
The coating of the print drum is very soft. It can be
easily scratched or chipped. Once the print drum has a
scratch or chip in it, that area will show up as a blotch
or line on all subsequent copies. Also, any of the rollers
can get bent, scratched, or develop some type of
irregularity and cause blotches. How do you determine
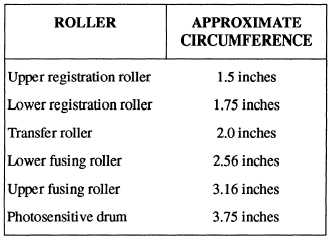
what part failed? All of the rollers and the drum shown
in figure 12-13 are different sizes. By measuring the
spacing between the blotches on the paper, you can get
a fairly good idea which area has the problem. Table
12-3 lists the approximate circumferences of the rollers
in most laser printers.
Laser Printer Page Languages
Currently there are two basic types of desktop laser
printers, the Hewlett-Packard (HP) and the Adobe
PostScript. Each has its own page description language.
Just about all laser printers use or emulate one of these
two languages.
HEWLETT-PACKARD SYSTEM.— When
Hewlett-Packard developed its LaserJet series of
printers, the fonts were largely developed from the
existing dot matrix printer bit maps. A bitmap is a table
that tells the printer when and where to place the dots.
With the Hewlett-Packard system, a font definition is
required for each font to be printed. Fonts can be
resident in the printer’s ROM, contained in a font
cartridge which holds additional ROMs, or they can be
soft fonts. Soft fonts are loaded into your computer’s
memory and transferred to the printer’s RAM as they
are needed.
Table 12-3.—Laser Printer Roller Circumferences
These printers offer very high resolution, a large
variety of fonts, and the capability to print graphics.
Depending on the model and manufacturer, the
Hewlett-Packard and compatible laser printers, can
print from four to eight pages of text per minute.
Printing graphics can slow down the printer
considerably.
POSTSCRIPT PRINTERS.— The PostScript
family of printers, developed by Adobe Systems, uses
an entirely different method for defining characters and
graphics. Where the HP system needed a definition for
each size font, the PostScript printer needs only one
definition for each character in a character set. The
definition of the font is a series of mathematical
calculations instead of a fixed number of dots. From
this definition, the PostScript printer uses mathematical
scaling of the character to print it any size from 5 to
5,000 points.
By being described mathematically, the image can
be manipulated in a number of ways. It can be rotated,
shrunk, expanded, twisted, shadowed, or placed in a
3-dimensional prospective.
With the exception of how characters are defined,
the basics of the PostScript printer are the same as the
HP printer. They both use the same print mechanisms
and interfaces.
ELECTROTHERMAL
PRINTERS
Electrothermal printers use the heat of wires or pins
to create images on a special heat sensitive paper. The
paper changes color when exposed to heat, allowing the
characters to appear.
INK JET PRINTERS
Ink jet printers form images and characters by
spraying fine drops of ink on the paper. The most
common type of inkjet printer is the drop-on-demand
print head. Drop-on-demand printing means that ink
is ejected out of the nozzles as needed.
12-13