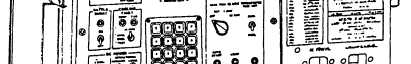
l Operator console —Controls operation of the
computer at the computer. This console/panel is
usually located above the logic chassis but separate
from the maintenance console/panel. It contains the
controls and indicators necessary to initiate computer
operations. You can turn on power to the system and
load the operational program and start its execution.
. Remote console —Controls operation of the
computer from a remote location. Performs the same
functions as an operator console except it does not apply
power to computer set.
l Maintenance console panel/display control unit
(DCU) —Controls operation of the computer and is
used to perform maintenance (preventive and
corrective).
l Specific power requirements (frequency and
voltage).
l Specific cooling requirements (air and/or liquid
cooling).
Minicomputers
Minicomputers are mid-range computers. They are
smaller in physical size than the large mainframes used
for tactical and tactical support operations. They are
also built for ruggedness. Minicomputers are capable
of stand-alone or self-contained operation, or of being
an embedded processor in a system or other type of
digital device. Minicomputers are generally used in
applications that don’t require the faster computational
speeds or larger memory capacities available on
mainframes.
These computers also have program
flexibility. Minicomputers receive external technical
support for the operational programs they use. The
programs for minicomputers are updated as specific
jobs or applications are updated and revised.
Some examples of minicomputers are the minis
used as interface computers with communications or
radar systems.
Minis are also used as the host
computers for the Shipboard Nontactical ADP Program
(SNAP I, SNAP II, and SNAP III) Systems. Training
for minicomputers is provided through formal A, C, and
FTC schools and may be NEC producing. SNAP
system training is an example of an NEC-producing
school. Figure 1-4 is an illustration of a typical
minicomputer.
Some physical features of minicomputers are
highlighted as follows:
Figure 1-4.—Example of a minicomputer.
1-5