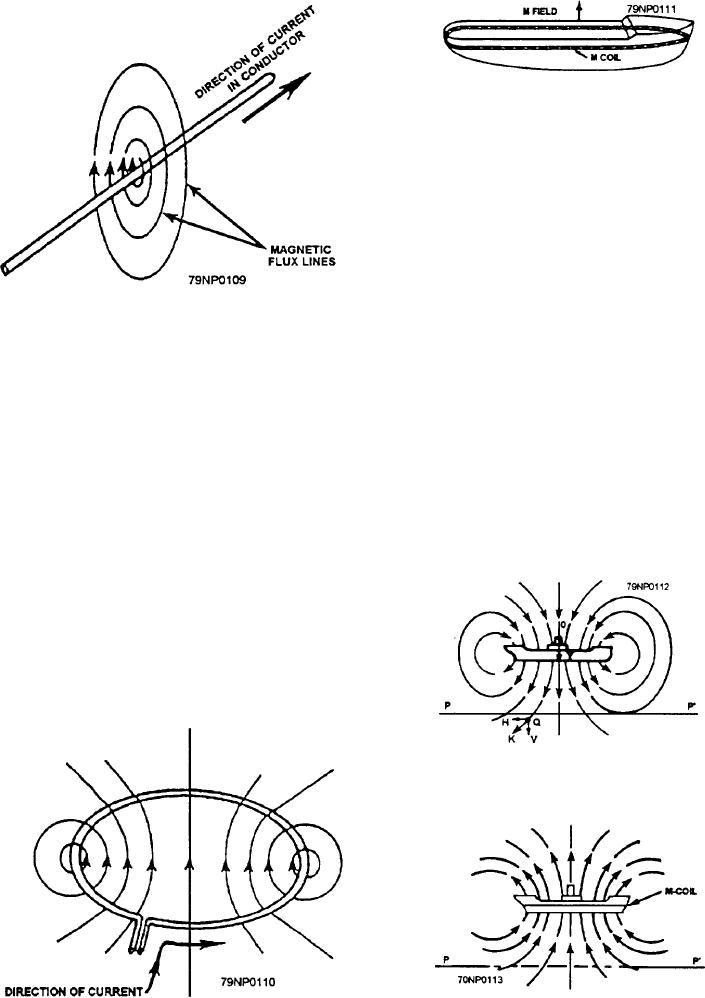
Figure 10-5.--M coil.
to the components of the ship's field. Each coil consists
of the main loop and may have smaller loops within the
area covered by the main loop, usually at the same level.
The smaller loops oppose localized peaks that occur in
the ship's magnetic field within the area covered by the
main loop.
M Coil
Figure 10-3.--Magnetic field around a current-carrying
The M (main) coil (fig. 10-5) encircles the ship in a
conductor.
horizontal plane, usually near the waterline. The M coil
produces a magnetic field that counteracts the magnetic
Coil Function
field produced by the vetical permanent and vertical
induced magnetization of the ship.
Each of the components of the ship's magnetization
Figure 10-6 shows the magnetic field produced by
(horizontal, vertical, and athwartships) produces a
the vertical magnetization of the ship. Figure 10-7
magnetic field in the vicinity of the ship. Current
shows the magnetic field produced by the M coil. The
through a conductor produces a magnetic field around
M-coil field opposes the magnetic field produced by the
it (fig. 10-3). By forming the conductor into a coil, a
vertical magnetization of the ship. If the M-coil
magnetic field can be produced to surround the ship in
compensating magnetic field were everywhere exactly
specific areas (fig. 10-4). Strategically locating these
equal and opposite to the field produced by the vertical
coils and precisely controlling the magnitude and
polarity of the current through these coils will
effectively restore the earth's field to the undistorted
condition around the ship.
Each degaussing coil has the required location and
the number of turns to establish the required magnetic
field strength when it is energized by direct current of
the proper value and polarity. The coils will then
produce magnetic field components equal and opposite
Figure 10-6.--Magnetic field due to the vertical magnetization
of the ship.
Figure 10-4.--Magnetic field of a current-carrying coil.
Figure 10-7.--Magnetic field produced by the M coil.
10-6

