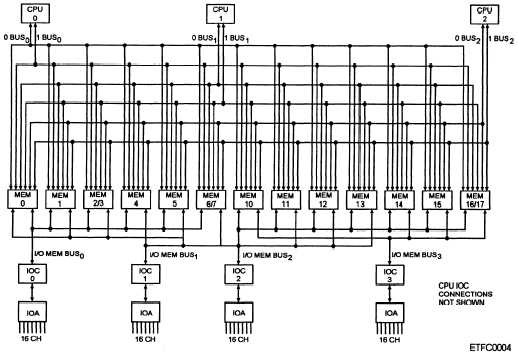
overall functional layout. Figure 2-4 is an example of
a functional layout of a multiconfiguration computer
system.
PHYSICAL LAYOUTS OF COMPUTERS
Physical layouts provide you with a “picture” of the
computer. They are designed to show what the
computer looks like and where each assembly, module,
or console (maintenance and operator) of the computer
is located. Physical layouts do NOT depict detailed
descriptions of signal flow. Let’s take a look at some of
the ways computers are physically laid out.
Overall Physical Layout of Computers
Overall physical layouts will show you where each
of the major parts of a single computer/computer set is
located. The physical layouts and the terminology will
vary with the type of computer and the manufacturer.
The technical manual of each computer will provide
you with the physical layout of that computer. Let’s
take a look at four types of physical layouts—modular,
chassis or assembly, cage or rack, and motherboard or
backplane.
MODULAR.— The functional areas of the
computer are modularized. In other words, the
functional areas only contain the hardware for the
function specified.
For example, the module
designated as the CPU only contains the subassemblies
or printed circuit boards for the CPU functions. Figure
2-5 is an example that depicts the physical layout of a
single mainframe computer set. Notice the modular
layout. Also keep in mind that data systems that employ
a multiple configuration will depict the minimum
physical layout configuration AND the full physical
layout configuration.
CHASSIS OR ASSEMBLY.— Chassis or
assemblies usually are door mounted or slide mounted.
Computers that use chassis or assemblies may contain
one or more chassis or assemblies for the whole system.
For example, one chassis may be dedicated only for
memory, one for the power supply, and a third chassis
or assembly for the rest of the computer (the CPU and
the I/O). One to several subassemblies or printed circuit
boards (pcb’s) may comprise the CPU, I/O, or memory.
Figure 2-6 is an illustration of a chassis used in a
minicomputer.
CARD CAGE OR RACK.— A card-cage or
rack-designed computer will generally contain the
major functional areas of a computer. The card cage or
rack is usually centrally mounted in the overall
computer chassis.
The number of subassemblies or
pcb’s contained in a card cage or rack can vary from just
a few to many depending on the technology of the
computer. One or more pcb’s may comprise a
functional area. A card cage or rack is fixed in a single
position; it does not slide out or swing open like a door.
Figure 2-4.—Example of a functional layout of a multiconfiguration computer system.
2-4