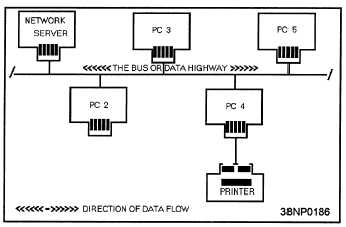
messages must pass through the other workstations on
the way to their destinations. Each node checks the
address attached to the message to see if it matches its
own address. Bus topologies allow individual nodes
to be out of service or to be moved to new locations
without disrupting service to the remaining nodes.
Because of the way linear bus cabling is laid out,
this type of network is simple. The bus topology is
very reliable, because if any node on the bus network
fails, the bus itself is NOT affected, and the remaining
nodes can continue to operate without interruption.
Many of the low cost LANs use a bus topology and
twisted-pair wire cabling.
Figure 8-2.—A bus network topology.
A disadvantage of the bus topology is that
generally there must be a minimum distance between
workstations to avoid signal interference. Another
disadvantage is that the nodes must conpete with each
other for the use of the bus. Simultaneous
transmissions by more than one node are N O T
permitted. This problem, however, can be solved by
using one of several types of systems designed to
control access to the bus. They are collision
detection, collision avoidance, and token passing,
which we will cover shortly. Also, there is no easy
way for the network administrator to run diagnostics
on the entire network. The bus network can be easily
compromised by an unauthorized user, since all
messages are sent along a common data bus. For this
reason, it is difficult to maintain network security.
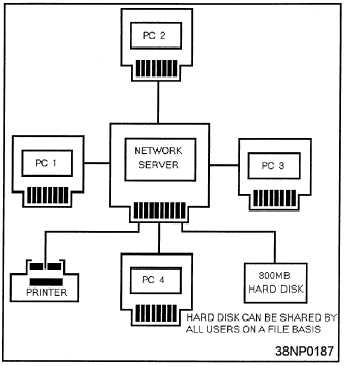
Figure 8-3.—A star network topology.
STAR NETWORK
In a star network, each component is connected
directly to the central computer or network server, as
shown in figure 8-3. Only one cable is required from
the central computer to each PC’s network interface
card to tie that workstation to the LAN. The star is
one of the earliest types of network topologies. It uses
the same approach to sending and receiving messages
as our phone system. Just as a telephone call from
one person to another is handled by a central
switching station, all messages must go through the
central computer or network server that controls the
flow of data. New workstations can be easily added
to the network without interrupting other nodes. This
is one of the advantages of the star topology.
Another advantage of star topology is that the
network administrator can give selected nodes a
higher priority status than others. The central
computer looks for signals from these higher priority
workstations before recognizing other nodes. The star
topology also permits centralized diagnostics
(troubleshooting) of all functions. It can do this
because all messages must first go through the central
8-8