is connected across phases B and C in series. Thus, the
voltage across each load is larger than the voltage across
a single phase. In a wye-connected ac generator, the
three start ends of each single-phase winding are
connected together to a common neutral point and the
opposite, or finish, ends are connected to the line
terminals, A, B, and C. These letters are always used to
designate the three phases of a three-phase system, or
the three line wires to which the ac generator phases
comect.
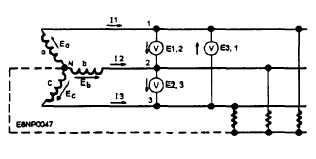
A three-phase, wye-connected ac generator
supplying three separate loads is shown in figure 3-13.
When unbalanced loads are used, a neutral may be
added as shown in the figure by the broken line between
the common neutral point and the loads. The neutral
wire serves as a common return circuit for all three
phases and maintains a voltage balance across the loads.
No current flows in the neutral wire when the loads are
balanced. This system is a three-phase, four-wire circuit
and is used to distribute three-phase power to
shorebased installations. The three-phase, four-wire
system is not used aboard ship, but it is widely used in
industry and in aircraft ac power systems.
Delta Connection
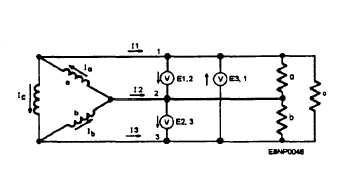
A three-phase stator may also be connected as
shown in figure 3-12, view C. This is called the delta
connection. In a delta-connected ac generator, the start
end of one phase winding is connected to the finish end
of the third; the start of the third phase winding is
connected to the finish of the second phase winding; and
the start of the second phase winding is connected to the
finish of the first phase winding. The three junction
points are connected to the line wires leading to the load.
A three-phase, delta-connected, ac generator is
depicted in figure 3-14. The generator is connected to
a three-phase, three-wire circuit, which supplies a
three-phase, delta-connected load at the right-hand end
of the three-phase line. Because the phases are
connected directly across the line wires, phase voltage
Figure 313.—Three-phase ac generatar showing neutral
connection.
Figure 3-14.-Three-phase, delta-connected system.
is equal to line voltage. When the generator phases are
properly connected in delta, no appreciable current
flows within the delta loop when there is no external
load connected to the generator. If anyone of the phases
is reversed with respect to its correct connection, a
short-circuit current flows within the windings of no
load, causing damage to the windings.
TRANSFORMERS
A transformer is a device that has no moving parts
and that transfers energy from one circuit to another by
electromagnetic induction. The energy is always
transferred without a change in frequency, but usually
with changes in voltage and current. A step-up
transformer receives electrical energy at one voltage and
delivers it at a higher voltage. Conversely, a step-down
transformer receives energy at one voltage and delivers
it at a lower voltage. Transformers require little care and
maintenance because of their simple, rugged, and
durable construction. The efficiency of transformers is
high. Because of this, transformers are responsible for
the more extensive use of alternating current than direct
current.
The conventional constant-potential
transformer is designed to operate with the primary
connected across a constant-potential source and to
provide a secondary voltage that is substantially
constant from no load to full load.
Various types of small, single-phase transformers
are used in electrical equipment. In many installations,
transformers are used on switchboards to step down the
voltage for indicating lights. Low-voltage transformers
are included in some motor control panels to supply
control circuits or to operate overload relays.
Instrument transformers include potential, or
voltage, transformers and current transformers.
Instrument transformers are commonly used with ac
instruments when high voltages or large currents are to
be measured.
3-9